Shallow Foundation Malaysia
Home > Shallow Foundation Malaysia

Shallow Foundation Malaysia
Typically, a building or structure is divided into two main parts, which are the superstructure and the substructure.
The substructure or foundation transfers the load of the superstructure. The foundation, which is the lowest part of a structure, is intended to distribute the load evenly to the soil with the appropriate amount of pressure.
The load of the superstructure is transmitted either by columns or walls to the foundation or substructure.
Before deciding which type of building foundation is suitable, it is recommended to conduct a soil survey to determine the conditions of the ground. You could dig holes at different points throughout the site and assume the conditions based on the results.
The two types of foundations used in a construction are deep foundation and shallow foundation, depending on the depth of the soil where they are placed.
A deep foundation transfers loads a depth of over 1.5 meters below the ground surface, while a shallow foundation transfers loads no more than 1.5 meters underneath the surface.
Domestic projects and small buildings usually require shallow foundations where the depth is typically lesser than the width. They are suitable as a foundation for a house extension too.
Deep foundations are used for commercial and taller commercial buildings or construction on very weak ground to transfer the structure’s load from the weak soil to the stronger rock or soil underneath.
Purpose of a building foundation

Prevent the rise of the ground moisture

Helps spreading the structure’s weight over a large soil area

Prevent movement of the structure laterally

Keep the structure stable by being an anchor

Avoid settlement that is unequal
Purpose of a building foundation
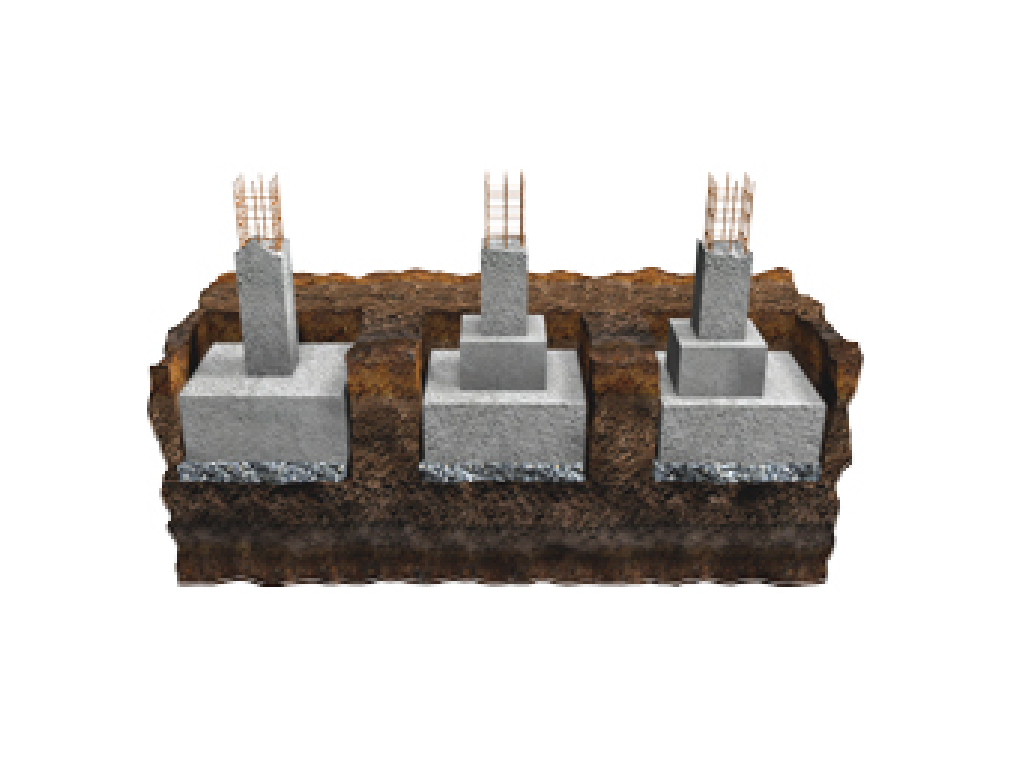

Isolated or individual footing
Also known as pad foundation or spread footing. In constructing a building, an isolated or individual footing is the most common type of foundation used, whereby it is built for a single column. It takes the shape of a circle, square or rectangle.
With uniform thickness, it is able to support and distribute concentrated loads. The calculation for its size is based on the ground conditions and load.
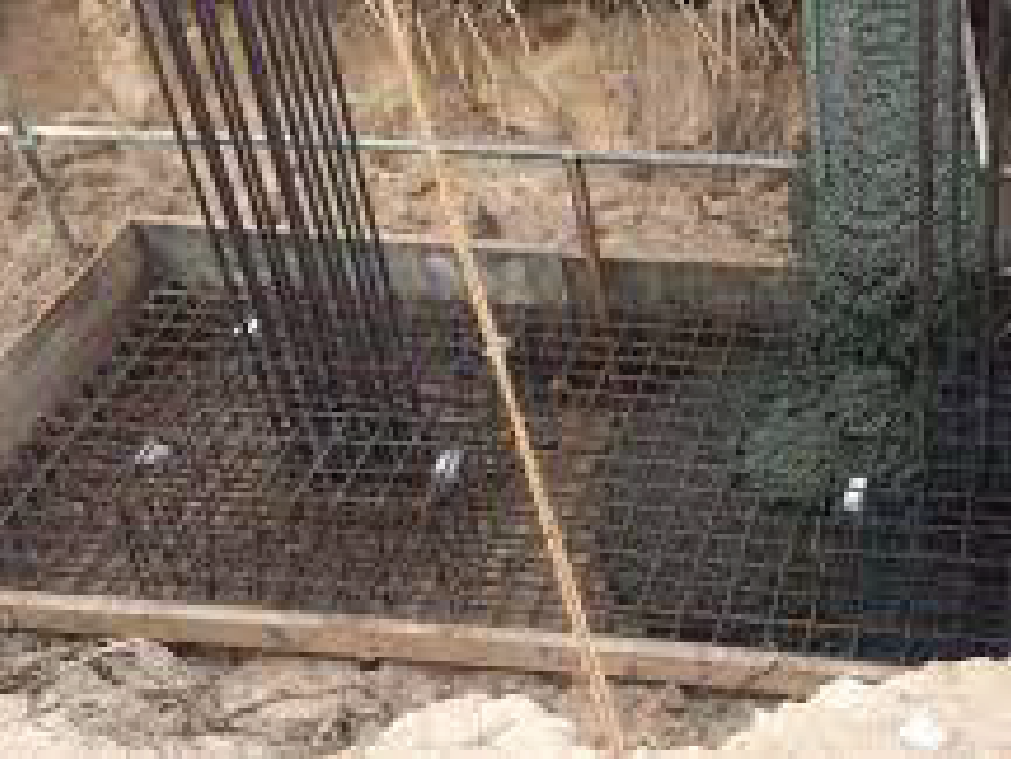

Combined footing
It generally takes the rectangular shape. The combined footing is constructed by overlapping the isolated footings of two columns close enough to each other. However, the structural design is still different.
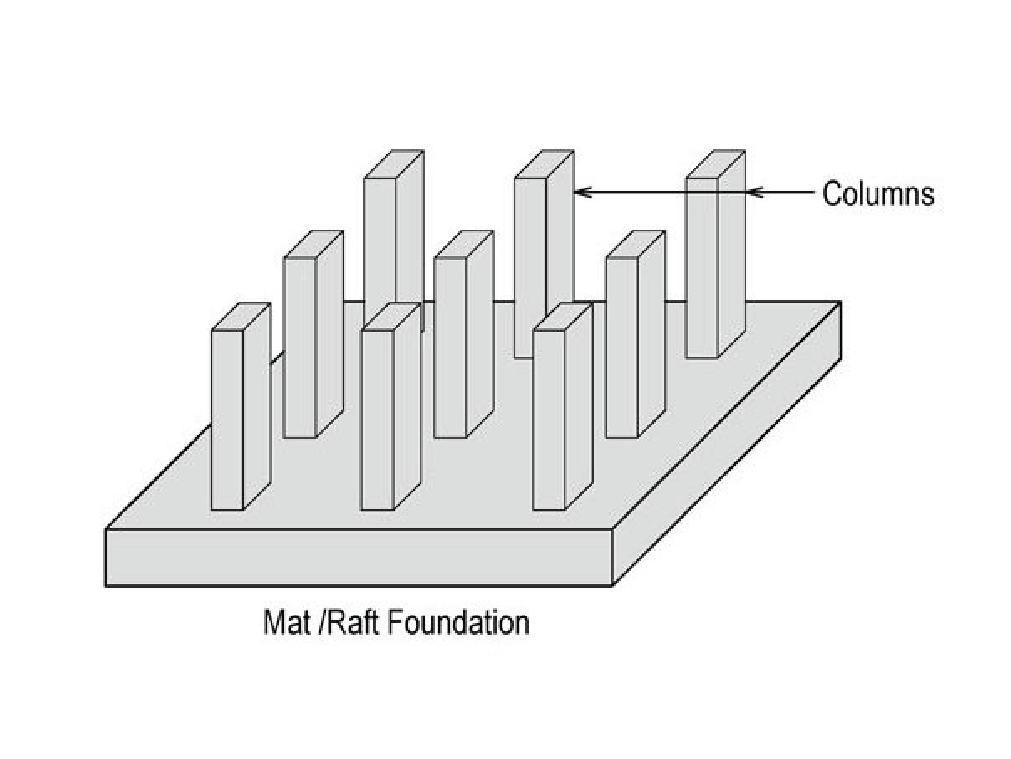
Raft or mat foundation
Raft or mat foundations are the types of foundations that span the entire area of a building, and therefore support the weight of the columns and walls.
This type of foundation is used when walls and columns are so close that individual footings would not be practical or cost-effective or when soil pressure is low.
The application of spread footings and wall footings is appropriate for expansive soils with less bearing capacity. With individual footings and wall footings, a raft foundation can be economically constructed when one-half of the area of a structure is covered.
In the case of columns and walls foundations where the structural loads on columns and walls are very high, this type of foundation is used too. As a result of this design, differential settlement of individual footings is prevented, with the structure being designed as one mat (or combined footing).
Address
No 35, Tingkat satu, Taman Sri Kluang 86000 Kluang, Johor, Malaysia
